ICEECE2012 Poster Presentations Clinical case reports - Thyroid/Others (81 abstracts)
Reversible Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: clinical, hormonal, autoimmune and ultrasonographic evidence
M. Niedziela
Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland.
Introduction: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) and Graves' disease (GD) constitute a spectrum of autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD). An abnormal thyroid echographic pattern characterized by a diffuse low echogenicity has been described in both AITD. This hypoechogenicity is due to three components: increase of intrathyroidal flow, functional changes in thyroid follicles with increased cellularity and decrease of the colloid content, resulting in the reduction of the cell/colloid interface, variable degree of lymphocytic infiltration. The first two components may be reversible during medical treatment and seem to be characteristic for GD, whereas lymphocytic infiltration may rather represent mostly HT.
Case report: A 19-year-old boy manifested initially, at the age of 15 years, the typical clinical signs of hyperthyroidism (excessive sweating, heat intolerance, sleep disturbances firm goiter (II degree), tachycardia, palpitations, nervousness, excessive sweating and tremor). Laboratory tests evidenced mild T3-dependent hyperthyroidism with decreased TSH and a positive titer of anti-TPO and anti-TG antibodies whereas TRAb were negative. Thyroid ultrasound (TUS) was heterogenous, predominantly hypoechogenic. Hashitoxicosis was diagnosed. 2.5 years later, after more than 1.5 years of no control, he was readmitted to the ward with clinical an hormonal features of hypothyroidism of autoimmune origin. Ultrasound examination showed hypoechogenicity of the gland and enhanced vascular flow based on Power Doppler analysis. L-thyroxine (
Declaration of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research project.
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
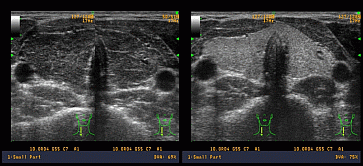
Figure 1.




